While the Satellite ID's displayed on this page were current at the time of publication, all remaining information continues to be relevant. Updated WAAS-EGNOS satellite identification information can be found here.
WAAS
What is WAAS?
- WAAS is the acronym for the Wide Area Augmentation System developed by the FAA and the DOT to give aircraft the ability to rely on GPS for all phases of flight by improving GPS accuracy, integrity, and availability.
How does WAAS work?
- A network of ground based wide area reference stations (WRS) monitor GPS satellite signals for variations caused by atmospheric disturbances, clock drift, and satellite orbit errors.
- The WRS relay these errors to wide area master stations (WMS) where the deviation correction (DC) information is computed, and updated correction messages are transmitted to geosynchronous satellites via a ground uplink system (GUS) every five seconds or better.
- These geosynchronous satellites then broadcast the correction data back to Earth where any WAAS enabled receiver can use the information to improve reported position accuracy.
WAAS coverage
- WAAS coverage currently extends to portions of North America, Alaska, and Hawaii.
Do I need WAAS?
- Unless you will be piloting an aircraft over the U.S. any time soon, probably not. However, the Garmin Oregon 6x0 is WAAS enabled, and you can still use WAAS to more accurately plot your position on Earth, so why not? Besides, you didn't buy a GPS receiver because you thought paper maps and a compass were 'close enough', now did you?
WAAS Satellite Map
![WAAS SAT Map [2010-03].jpg WAAS SAT Map [2010-03].jpg](https://www.gpsrchive.com/Oregon 6xx/files/WAAS%20SAT%20Map%20%5B2010-03%5D.jpg)
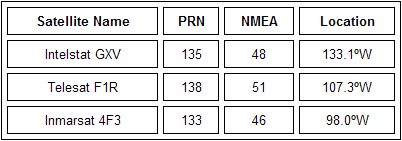
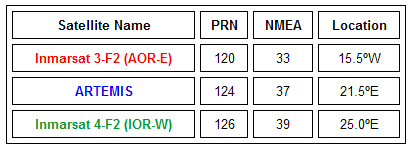
- PRN is the satellites actual Psuedo-Random Noise code.
- NMEA is the satellite number referenced by some GPS receivers (NMEA = PRN - 87).
WAAS on Oregon 6x0
- Enable WAAS in [Setup > System > WAAS/EGNOS].
- Disable Battery Save in [Setup > Display > Battery Save].
- Open the Satellite application.
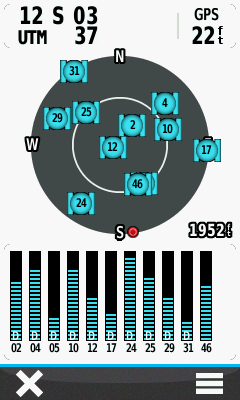
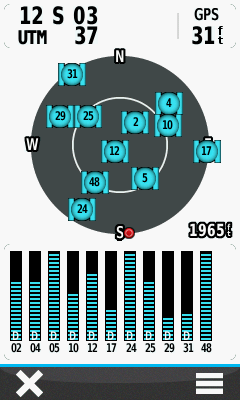
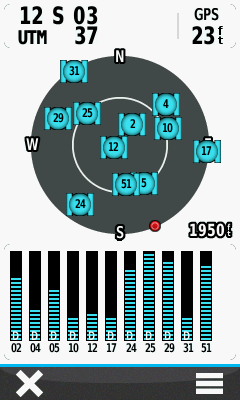
- Only with WAAS enabled will signal bars be present for satellites 46, 48 or 51:
 |
 |
 |
||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ==/== |
Receiving WAAS correction data from satellite 46, located about 47º above the horizon in a south south east direction. |
==/== |
WAAS correction data is provided courtesy of satellite 48, approximately 45º above the south west horizon. |
==/== |
Satellite 51 is transmitting WAAS correction data almost directly from the south and nearly 50º above the horizon. |
EGNOS
What is EGNOS?
- The European Geostationary Navigation Overlay Service is a satellite based augmentation system (SBAS) developed by the European Space Agency, the European Commission, and EUROCONTROL to supplement the GPS, GLONASS and Galileo systems by reporting on the reliability and accuracy of their signals.
How does EGNOS work?
- Similar to WAAS, the EGNOS system consists of three geostationary satellites and a network of ground stations.
-
More than 40 ground stations are linked together to create the EGNOS network consisting of:
- 34 RIMS (Ranging and Integrity Monitoring Stations) - receiving signals from US GPS satellites,
- 4 MCC (Mission Control Centers) - data processing and differential corrections counting,
- 6 NLES (Navigation Land Earth Stations) - accuracy and reliability data sending to three geostationary satellite transponders to allow end-user devices to receive them.
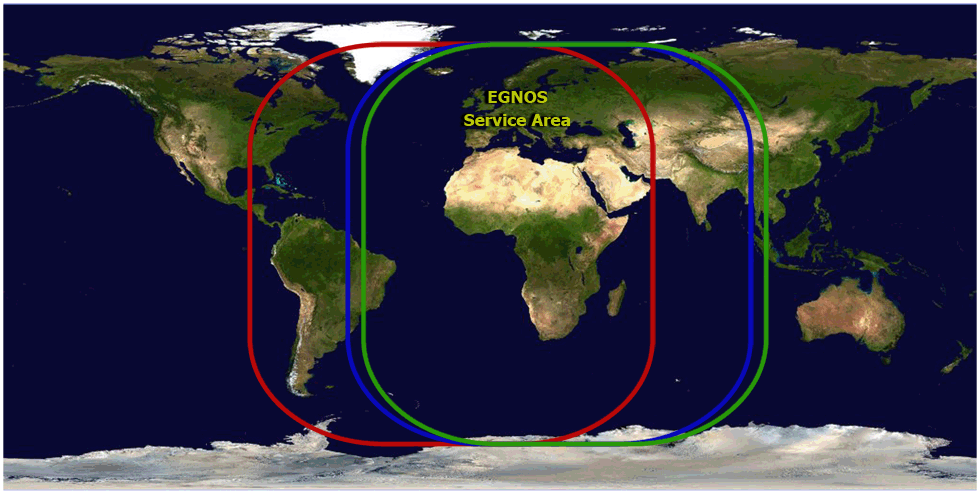
EGNOS coverage
- EGNOS coverage currently extends to parts of Europe and Africa.
Do I need EGNOS?
- Yes, for the same reasons others need WAAS.
EGNOS Satellite Map
- PRN is the satellites actual Psuedo-Random Noise code.
- NMEA is the satellite number referenced by some GPS receivers (NMEA = PRN - 87).
EGNOS on Oregon 6x0
- Enable EGNOS in [Setup > System > WAAS/EGNOS].
- Disable Battery Save in [Setup > Display > Battery Save].
- Open the Satellite application.
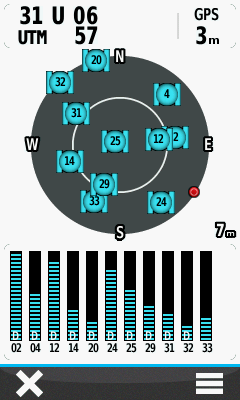
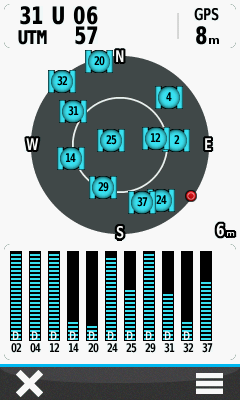
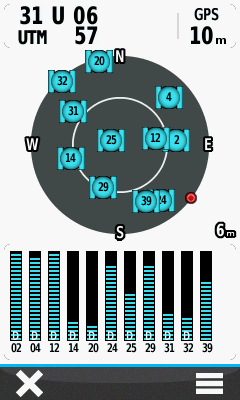
- Only with EGNOS enabled will signal bars be present for satellites 33, 37 or 39:
 |
 |
 |
||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ==/== |
Receiving EGNOS correction data from satellite 33, located approximately 32º above the south south west horizon. |
==/== |
EGNOS correction data provided courtesy satellite 37, approximately 30º above the south south east horizon. |
==/== |
Satellite 39 also transmits EGNOS correction data from about 30º above the south south east horizon. |