What is BeiDou?
- BeiDou (BDS) was created by the Chinese government to provide global access to high accuracy positioning, navigation and timing services.
- BeiDou was named after the asterism commonly known as the Big Dipper, consisting of the seven brightest stars in the Ursa Major (or Great Bear) constellation that have been used for navigation since ancient times.
BeiDou Operation
-
Construction of the BeiDou system was divided into three stages:
- BDS-1 consisted of three satellites that provided limited coverage and services to the China region from 2000 through 2012.
-
BDS-2 (formerly known as COMPASS) began providing services to China in December
2011, and the Asia-Pacific region in December 2012.
- Constellation consists of 5 GEO, 5 IGSO, and 4 MEO satellites.
- Provides three public service signals across three frequency bands
(B1, B2, B3):
- B1 Signal: 1561.098 MHz
- B2 Signal: 1207.140 MHz
- B3 Signal: 1268.520 MHz
-
BDS-3 started providing global services in December of 2018, with the 35th
and final satellite launched in March of 2020.
- Constellation consists of 3 GEO, 3 IGSO, and 24 MEO satellites.
- Provides five public service signals across three frequency bands
(B1, B2, B3):
- B1I Signal: 1561.098 MHz
- B1C Signal: 1575.420 MHz
- B2a Signal: 1176.450 MHz
- B2b Signal: 1207.140 MHz
- B3 Signal: 1268.520 MHz
BeiDou Services
- The BeiDou system provides the following services:
- Open Service
- Satellite Based Augmentation Service
- Short Message Communication Service
- Precise Point Positioning Service
- Search and Rescue Service
BeiDou Coverage
- BeiDou employs a combination of satellites in MEO, GEO and IGSO orbits to provide global Earth coverage.

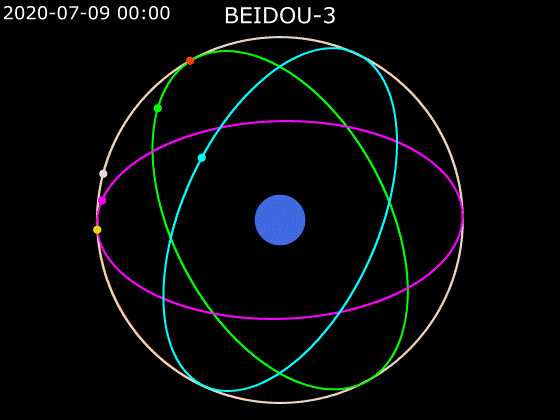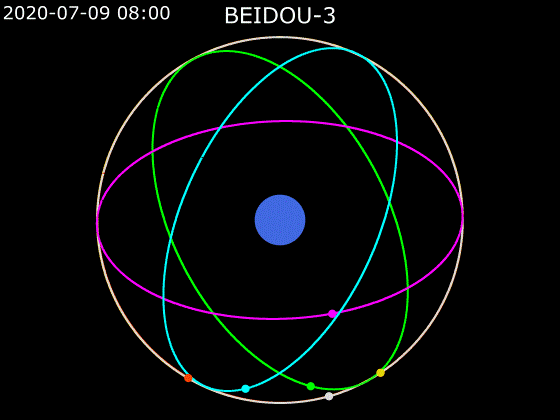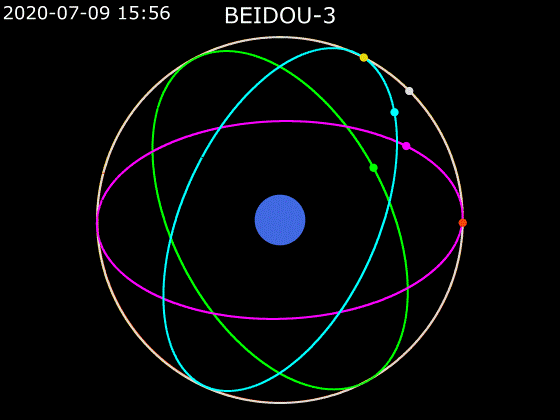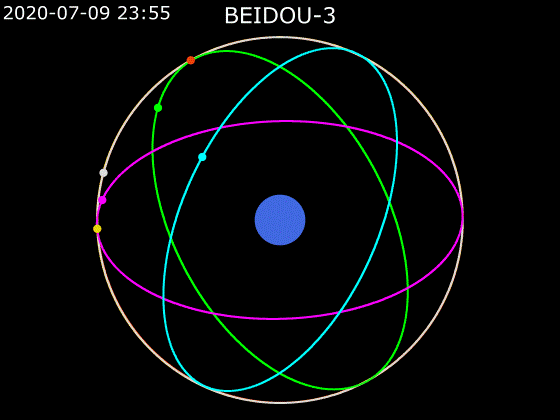
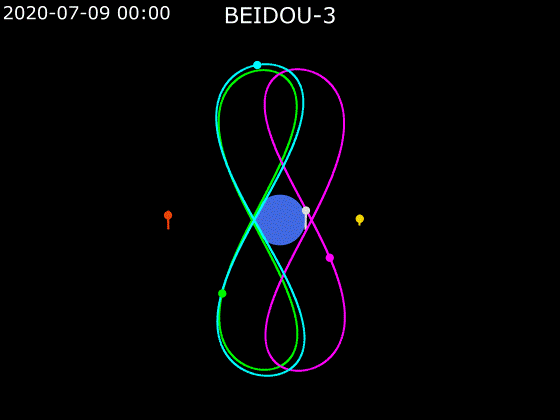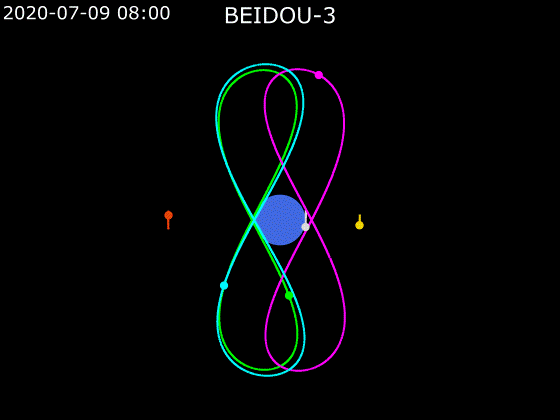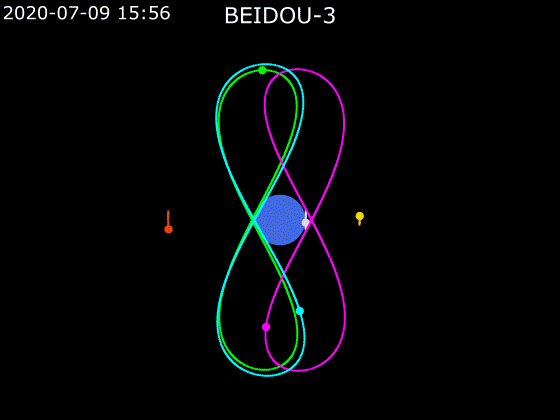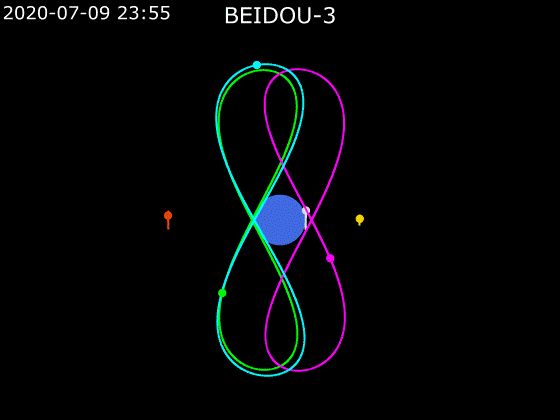
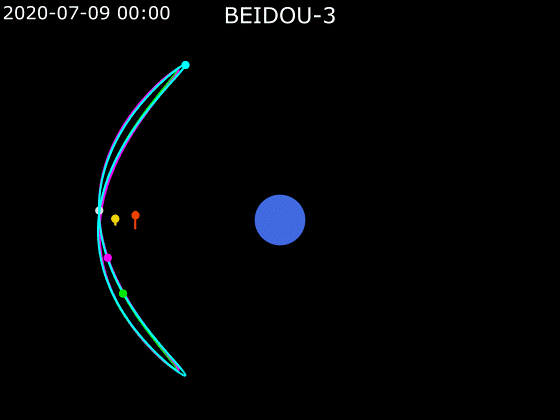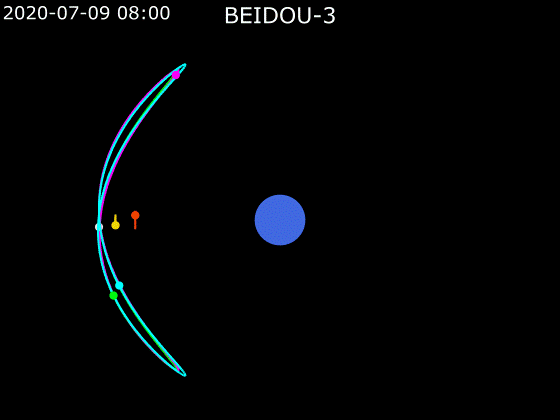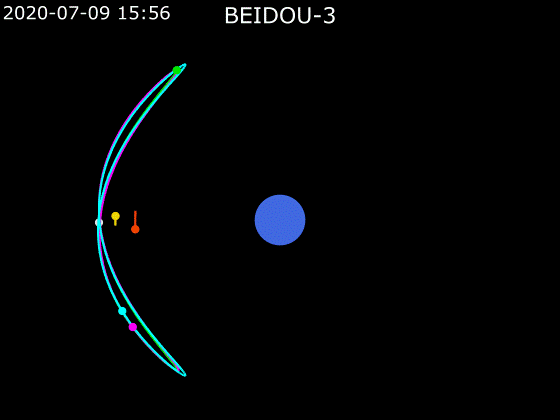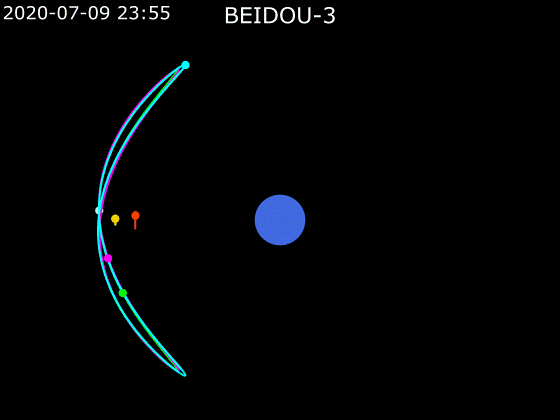
MEO + GEO
oblique viewMEO + GEO
polar viewIGSO
equatorial front viewIGSO
equatorial side view

BeiDou Availability
- Global positioning services became available on 27 December 2018.
- A complete 35-satellite BeiDou system was completed on 23 June 2020.
- As of January 2022, the BeiDou constellation consisted of 44 operational satellites:
- GEO (GEostationary Orbit): 7
- IGSO (Inclined GeoSynchronous Orbit) 55°: 10
- MEO (Medium Earth Orbit): 27
- View a list of available BeiDou satellites. (status)
- Choose desired BeiDou Satellite (NMEA ID) below to view current location:
Do I Need BeiDou?
- Many modern GPS receivers (GPSr) are capable of receiving BeiDou satellite signals.
- With more operational satellites in orbit than any other system, BeiDou can provide improved coverage and accuracy.
- BeiDou provides an accuracy of 3.6m for global public use, 2.6m for Asia Pacific, and 10cm for encrypted users.
- Additional BeiDou benefits include improved security, high reliability and bi-directional communication capabilities.